The clinical and immunological features of pediatric COVID-19 patients in China.
In December 2019, the corona virus illness 2019 (COVID-19) attributable to novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) emerged in Wuhan, China and quickly unfold worldwide. Few info on clinical features and immunological profile of COVID-19 in paediatrics.
The clinical features and remedy outcomes of twelve paediatric patients confirmed as COVID-19 have been analyzed. The immunological features of kids patients was investigated and in contrast with twenty grownup patients.
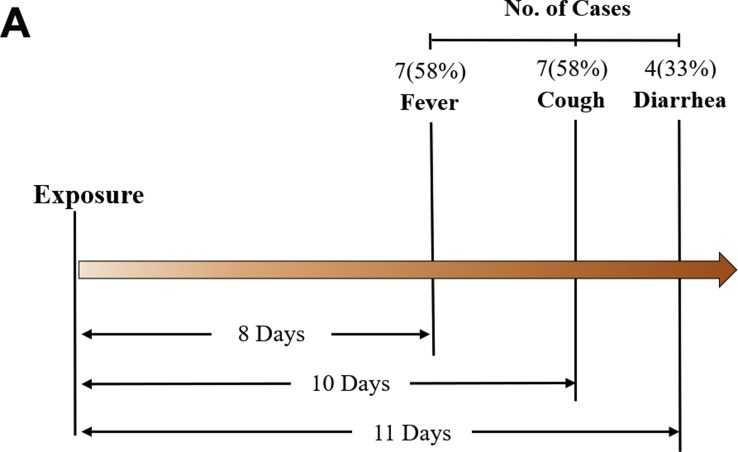
The median age was 14.5-years (vary from 0.64 to 17), and six of the patients have been male. The common incubation interval was Eight days. Clinically, cough (9/12, 75%) and fever (7/12, 58.3%) have been the commonest signs.
Four patients (33.3%) had diarrhea through the illness. As to the immune profile, kids had greater quantity of whole T cell, CD8+ T cell and B cell however decrease CRP ranges than adults (P < 0.05). Ground-glass opacity (GGO) and native patchy shadowing have been the everyday radiological findings on chest CT scan. All patients acquired antiviral and symptomatic remedy and the symptom relieved in 3-Four days after admitted to hospital.
The paediatric patients confirmed delicate symptom however with longer incubation interval. Children contaminated with SARS-CoV-2 had totally different immune profile with greater T cell quantity and low inflammatory components stage, which could ascribed to the delicate clinical symptom.
We advise that nucleic acid check or examination of serum IgM/IgG antibodies in opposition to SARS-CoV-2 ought to be taken for kids with publicity historical past regardless of clinical symptom.
Clinical features of pediatric patients with coronavirus illness (COVID-19).
Coronavirus illness 2019 (COVID-19) attributable to SARS-CoV-2 has unfold world wide, and studies of kids with COVID-19 are growing.To assess clinical profiles of pediatric COVID-19.A retrospective evaluation was undertaken utilizing clinical information of sixteen kids (11 months-14 years) identified with COVID-19 between January 1, 2020 and March 17, 2020 at Xiangyang Central Hospital, Hubei province, China.
All kids had optimistic epidemiologic histories, 12 (12/16, 75 %) involving household models. The sicknesses have been both delicate (5/16, 31.3 %) or peculiar (11/16, 68.8 %), presenting as follows: asymptomatic (8/16, 50 %), fever and/or cough (8/16, 50 %).
Four asymptomatic patients (4/16, 25 %) in peculiar circumstances had chest computed tomography (CT) abnormalities. Leukocyte counts have been regular in 14 circumstances(88 %), however 2 patients (12.5 %) had leukopenia, and 1 (6.3 %) was lymphopenic.
There have been 11 patients with chest CT abnormalities, some nodular, others small patchy and others ground-glass opacities. In asymptomatic kids, the median time to SRAS-CoV-2 nucleic acid check(NAT) positivity as soon as uncovered to a member of the family with confirmed an infection was 15.5 days (vary, 10-26 days).
The median time to first NAT-negative conversion was 5.5 days (vary, 1-23 days).COVID-19 in kids of Xiangyang metropolis is commonly household acquired and not critical, with favorable outcomes. Asymptomatic kids may be identified as pneumonia as a result of of chest CT abnormalities. It is important to actively display this phase of the inhabitants.